The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
AAPG Bulletin
Figure
AAPG Bulletin; Year: 2015; Issue: June DOI: 10.1306/01191513190
Return to Full Text

Figure 2
Examples of clinoforms produced by the clinoform-modeling algorithm conditioned to different bounding surfaces and clinoform geometries. (A) Bounding surfaces represent postdepositional compaction and folding of the original (depositional) geometries of the clinoform and the top and base bounding surfaces. (B) Bounding surfaces represent a clinoform within a volume truncated at its top, for example, by a channel (Figure 1). (C) Bounding surfaces represent a clinoform downlapping onto irregular sea-floor topography. (D) Height function, 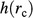 (equation 1; see Table 1 for nomenclature). (E) Shape function,
(equation 1; see Table 1 for nomenclature). (E) Shape function, 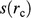 (equation 7; Table 1), demonstrating that increasing the exponent,
(equation 7; Table 1), demonstrating that increasing the exponent, 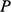 , increases the dip angle of clinoforms.
, increases the dip angle of clinoforms.

Figure 2
Examples of clinoforms produced by the clinoform-modeling algorithm conditioned to different bounding surfaces and clinoform geometries. (A) Bounding surfaces represent postdepositional compaction and folding of the original (depositional) geometries of the clinoform and the top and base bounding surfaces. (B) Bounding surfaces represent a clinoform within a volume truncated at its top, for example, by a channel (Figure 1). (C) Bounding surfaces represent a clinoform downlapping onto irregular sea-floor topography. (D) Height function, (equation 1; see Table 1 for nomenclature). (E) Shape function,
(equation 7; Table 1), demonstrating that increasing the exponent,
, increases the dip angle of clinoforms.
