About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Journal of Sedimentary Research (SEPM)
Abstract
Dolomitization of a  Carbonate
Carbonate Platform During Late Burial: Lower to Middle Cambrian Shady Dolomite, Virginia Appalachians
Platform During Late Burial: Lower to Middle Cambrian Shady Dolomite, Virginia Appalachians
Roger J. Barnaby (2), J. Fred Read
ABSTRACT
Outer platform carbonates of the Lower to Middle Cambrian Shady Dolomite, Virginia Appalachians, record a lengthy and complex diagenetic history, ranging  from
from marine cementation to burial diagenesis during late Paleozoic overthrusting. Analysis of petrographically well-preserved marine cements has provided an estimate of the isotopic composition of Lower Cambrian marine
marine cementation to burial diagenesis during late Paleozoic overthrusting. Analysis of petrographically well-preserved marine cements has provided an estimate of the isotopic composition of Lower Cambrian marine  carbonate
carbonate (
(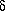 18O = -7.5 to -6.1
18O = -7.5 to -6.1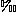 PDB;
PDB; 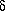 13C = +0.2 to +0.8
13C = +0.2 to +0.8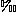 PDB; 87Sr/86Sr = 0.70869 to 0.70975), establishing a base line with which to assess later diagenetic
PDB; 87Sr/86Sr = 0.70869 to 0.70975), establishing a base line with which to assess later diagenetic  carbonate
carbonate . Meteoric dissolution and early calcite cement postdate marine cementation and formed during subaerial exposure.
. Meteoric dissolution and early calcite cement postdate marine cementation and formed during subaerial exposure.
The platform margin carbonates were extensively dolomitized; dolomitization postdates calcite cementation and the initial development of stylolites and tectonic fractures. Several episodes of dolomite replacement and cementation are evident. Zone 1 dolomite consists of rare relict dolomite cores which were replaced and overgrown by zone 2A dolomite, the dominant replacement phase. Zone 2A dolomite is depleted in 18O (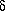 18O = -10.2 to -7.0) and enriched in 13C (
18O = -10.2 to -7.0) and enriched in 13C (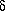 13C = +1.0 to +1.6) relative to marine
13C = +1.0 to +1.6) relative to marine  carbonate
carbonate , reflecting precipitation
, reflecting precipitation  from
from warm formation fluids buffered by the host
warm formation fluids buffered by the host  carbonate
carbonate . Uniformly low Sr contents (25 to 65 ppm) and
nonradiogenic 87Sr/86Sr (0.70900 to 0.70971) also attest to pore water equilibration with the host rock.
. Uniformly low Sr contents (25 to 65 ppm) and
nonradiogenic 87Sr/86Sr (0.70900 to 0.70971) also attest to pore water equilibration with the host rock.
Replacement dolomitization was followed by widespread  carbonate
carbonate dissolution, which formed vuggy porosity and local solution breccias. The host dolomite locally is encrusted by Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) occurrences of ore mineralization consisting of sphalerite, galena, and pyrite. This major generation of ore minerals is overgrown by three generations of dolomite cement. The first dolomite cement, zone 2B, has similar 18O composition (
dissolution, which formed vuggy porosity and local solution breccias. The host dolomite locally is encrusted by Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) occurrences of ore mineralization consisting of sphalerite, galena, and pyrite. This major generation of ore minerals is overgrown by three generations of dolomite cement. The first dolomite cement, zone 2B, has similar 18O composition (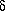 13O = -10.3 to -7.4) but slightly depleted 13C values (
13O = -10.3 to -7.4) but slightly depleted 13C values (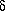 13C = +0.4 to +1.1) relative to zone 2A dolomite and has similar Sr contents (30 to 45 ppm) and 87Sr/86Sr ratios (0.70933
to 0.70966). Zone 2B dolomite cement exhibits petrographic, isotopic, and geochemical affinities with zone 2A replacement dolomite, implying that the two dolomite types formed
13C = +0.4 to +1.1) relative to zone 2A dolomite and has similar Sr contents (30 to 45 ppm) and 87Sr/86Sr ratios (0.70933
to 0.70966). Zone 2B dolomite cement exhibits petrographic, isotopic, and geochemical affinities with zone 2A replacement dolomite, implying that the two dolomite types formed  from
from fluids of similar composition and temperature. Primary fluid inclusions in zone 2B dolomite indicate precipitation
fluids of similar composition and temperature. Primary fluid inclusions in zone 2B dolomite indicate precipitation  from
from warm (minimum 120 to 150°C) brines (23-26 wt. % NaCl equiv.). These temperatures imply that the dolomitizing fluid was enriched in 18O due to extensive water-rock interaction with host
warm (minimum 120 to 150°C) brines (23-26 wt. % NaCl equiv.). These temperatures imply that the dolomitizing fluid was enriched in 18O due to extensive water-rock interaction with host  carbonate
carbonate , which also buffered the fluid
, which also buffered the fluid 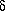 13C, Sr, and 87Sr/86Sr content.
13C, Sr, and 87Sr/86Sr content.
Zones 3 and 4 dolomite cement are depleted in 18O (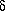 13O = -13.8 to -11.3) relative to the previous dolomites, implying a temperature increase to 150 to 210°C. The late dolomite cements have 13C compositions (
13O = -13.8 to -11.3) relative to the previous dolomites, implying a temperature increase to 150 to 210°C. The late dolomite cements have 13C compositions (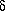 13C = -0.7 to +0.9) ranging
13C = -0.7 to +0.9) ranging  from
from those similar to the earlier dolomites to more depleted values. Zones 3 and 4 dolomite cement are enriched in Sr (60 to 135 ppm) which is radiogenic (87Sr/86Sr = 0.71025 to 0.71445). These later cements thus record fluids that were no longer buffered by the host
those similar to the earlier dolomites to more depleted values. Zones 3 and 4 dolomite cement are enriched in Sr (60 to 135 ppm) which is radiogenic (87Sr/86Sr = 0.71025 to 0.71445). These later cements thus record fluids that were no longer buffered by the host  carbonate
carbonate .
.
Dolomite cements locally were overgrown by sphalerite, followed by  authigenic
authigenic quartz and calcite cement. Secondary three phase fluid inclusions in quartz and calcite indicate hot (175 to 225°C) saline (30 to 33 wt. % NaCl equiv.) fluids. Temperatures and pressures interpreted
quartz and calcite cement. Secondary three phase fluid inclusions in quartz and calcite indicate hot (175 to 225°C) saline (30 to 33 wt. % NaCl equiv.) fluids. Temperatures and pressures interpreted  from
from the fluid inclusions are compatible with estimated burial depths in excess of 5 km.
the fluid inclusions are compatible with estimated burial depths in excess of 5 km.
The dolomites formed during deep burial, coeval with late Paleozoic, Alleghanian-age thrusting. The Mg required for burial dolomitization was derived  from
from pressure solution of structurally lower, platform interior dolomites that were overridden by the Shady Dolomite thrust sheet. Tectonic uplift and deformation resulted in regional fluid flow, which transported this Mg to the Shady Dolomite outer platform during burial dolomitization.
pressure solution of structurally lower, platform interior dolomites that were overridden by the Shady Dolomite thrust sheet. Tectonic uplift and deformation resulted in regional fluid flow, which transported this Mg to the Shady Dolomite outer platform during burial dolomitization.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 | |
| Open PDF Document: $24 |

