About This Item
- Full text of this item is not available.
- Abstract PDFAbstract PDF(no subscription required)
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Houston Geological Society Bulletin
Abstract
Abstract: Jurassic Cotton Valley  Reservoir
Reservoir
 Quality
Quality , Eastern
Offshore Gulf of Mexico: Chlorite Coatings and the
Porosity Preservation Story Found Below 20,000 ft
, Eastern
Offshore Gulf of Mexico: Chlorite Coatings and the
Porosity Preservation Story Found Below 20,000 ft
 Reservoir
Reservoir
 Quality
Quality , Eastern
Offshore Gulf of Mexico: Chlorite Coatings and the
Porosity Preservation Story Found Below 20,000 ft
, Eastern
Offshore Gulf of Mexico: Chlorite Coatings and the
Porosity Preservation Story Found Below 20,000 ftBy
1 Chevron Energy Technology Company, Houston, Texas
2 Chevron GOM Business Unit, New Orleans, Louisiana
3 Geocosm, Austin, Texas
The Jurassic Cotton Valley formation was penetrated near 20,000 ft in a shelf-margin growth-faulted well location in Viosca Knoll Block 251. The sands cored in the subject well describe three shallow water parasequences, each having argillaceous transgressive rocks overlain by coarser-grained highstand sandstones.
Intergranular, intragranular and fracture
porosity are contained within these sandstones.
Log porosity ranges from 1% to 14%
overall, and core porosity ranges from 1.0% to 6.7%. Although
quartz is the main cement, chlorite grain coatings inhibit quartz
cement when they are well developed. Late fractures are partly
filled with quartz and carbonate cement, and
unfilled fractures are thought to enhance
 reservoir
reservoir deliverability.
deliverability.
Cotton Valley in the eastern Gulf of Mexico
(GOM) composition and diagenetic path
stand in contrast to the quartzarenites found
farther west on trend. Fluvial-deltaic Cotton
Valley sands deposited and
reworked in East Texas and North
Louisiana systems are highly quartz
cemented and contain few clay coatings.
 Reservoir
Reservoir
 quality
quality is driven by
quartz cement volume and
is driven by
quartz cement volume and  reservoir
reservoir viability is lost below 15,000 ft. In
contrast, progradational fluvialdeltaic
sands in Viosca Knoll are
lithic arkoses and contain muscovite
and biotite both as discrete mica
and as metamorphic rock fragments.
This sandstone composition
shift is related to proximal
Appalachian drainages and minor
strandplain reworking in the eastern
GOM. Biotite dissolution
influences the Cotton Valley diagenetic
pathway to one favoring
chlorite coatings and porosity
preservation below 20,000 ft.
viability is lost below 15,000 ft. In
contrast, progradational fluvialdeltaic
sands in Viosca Knoll are
lithic arkoses and contain muscovite
and biotite both as discrete mica
and as metamorphic rock fragments.
This sandstone composition
shift is related to proximal
Appalachian drainages and minor
strandplain reworking in the eastern
GOM. Biotite dissolution
influences the Cotton Valley diagenetic
pathway to one favoring
chlorite coatings and porosity
preservation below 20,000 ft.
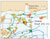 Unnumbered Figure. Location Map Showing the Deep Well Location in Viosca Knoll 251.
Unnumbered Figure. Location Map Showing the Deep Well Location in Viosca Knoll 251.
End_Page 55---------------
 Reservoir
Reservoir
 quality
quality uncertainty was constrained with Touchstone*
modeling. With the subject well as calibration, chlorite coatings
are shown to preserve
uncertainty was constrained with Touchstone*
modeling. With the subject well as calibration, chlorite coatings
are shown to preserve  reservoir
reservoir
 quality
quality to even greater depths.
to even greater depths.
EDITOR'S NOTE: *Touchstone is a software system for analysis of controls
on  reservoir
reservoir
 quality
quality in analog sandstones and for forward
modeling of sandstone diagenesis and petrophysical properties.
in analog sandstones and for forward
modeling of sandstone diagenesis and petrophysical properties.
End_of_Record - Last_Page 57---------------
 Unnumbered Figure. Upper Cotton Valley Depositional Systems Offshore Gulf of Mexico, Showing the Prograding Jurassic shelf.
Unnumbered Figure. Upper Cotton Valley Depositional Systems Offshore Gulf of Mexico, Showing the Prograding Jurassic shelf.