About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
AAPG Bulletin
Abstract
AAPG Bulletin, V.
2014. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists. All rights reserved.
DOI: 10.1306/09231313023
Experimental investigation of matrix  permeability
permeability of gas shales
of gas shales
 permeability
permeability of gas shales
of gas shales
Rob Heller,1 John Vermylen,2 and Mark Zoback3
1Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305; [email protected]
2Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305; [email protected]
3Department of Geophysics, Stanford University, Stanford, California 94305; [email protected]
ABSTRACT
Predicting long-term production  from
from gas shale reservoirs has been a major challenge for the petroleum industry. To better understand how production profiles are likely to evolve with time, we have conducted laboratory experiments examining the effects of confining stress and pore pressure on
gas shale reservoirs has been a major challenge for the petroleum industry. To better understand how production profiles are likely to evolve with time, we have conducted laboratory experiments examining the effects of confining stress and pore pressure on  permeability
permeability . Experiments were conducted on intact core samples
. Experiments were conducted on intact core samples  from
from the Barnett, Eagle Ford, Marcellus, and Montney shale reservoirs. The methodology used to measure
the Barnett, Eagle Ford, Marcellus, and Montney shale reservoirs. The methodology used to measure  permeability
permeability allows us to separate the reduction of
allows us to separate the reduction of  permeability
permeability with depletion (because of the resultant increase in effective confining stress) and the increase in
with depletion (because of the resultant increase in effective confining stress) and the increase in  permeability
permeability associated with Knudsen diffusion and molecular slippage (also known as Klinkenberg) effects at very low pore pressure. By separating these effects, we are able to estimate the relative contribution of both Darcy and diffusive fluxes to total flow in depleted reservoirs. Our data show that the effective
associated with Knudsen diffusion and molecular slippage (also known as Klinkenberg) effects at very low pore pressure. By separating these effects, we are able to estimate the relative contribution of both Darcy and diffusive fluxes to total flow in depleted reservoirs. Our data show that the effective  permeability
permeability of the rock is significantly enhanced at very low pore pressures (
of the rock is significantly enhanced at very low pore pressures (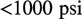 [
[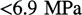 ]) because of the slippage effects. We use the magnitude of the Klinkenberg effect to estimate the effective aperture of the flow paths within the samples and compare these estimates to scanning electron microscopy image observations. Our results suggest effective flow paths to be on the order
]) because of the slippage effects. We use the magnitude of the Klinkenberg effect to estimate the effective aperture of the flow paths within the samples and compare these estimates to scanning electron microscopy image observations. Our results suggest effective flow paths to be on the order  from
from tens of nanometers in most samples to 100–200 nm, in a relatively high-
tens of nanometers in most samples to 100–200 nm, in a relatively high- permeability
permeability Eagle Ford sample. Finally, to gain insight on the scale dependence of
Eagle Ford sample. Finally, to gain insight on the scale dependence of  permeability
permeability measurements, the same core plugs were crushed, and
measurements, the same core plugs were crushed, and  permeability
permeability was again measured at the particle scale using the so-called Gas Research Institute method. The results show much lower
was again measured at the particle scale using the so-called Gas Research Institute method. The results show much lower  permeability
permeability than the intact core samples, with very little correlation to the measurements on the larger scale cores.
than the intact core samples, with very little correlation to the measurements on the larger scale cores.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $16 | |
| Open PDF Document: $28 |
AAPG Member?
Please login with your Member username and password.
Members of AAPG receive access to the full AAPG Bulletin Archives as part of their membership. For more information, contact the AAPG Membership Department at [email protected].
