About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Journal of Sedimentary Research (SEPM)
Abstract
Paleopedology and Stable Isotope Chemistry of Late Silurian Vertic Paleosols, Bloomsburg Formation, Central Pennsylvania
Steven G. Driese (2), Claudia I. Mora (2), Edward Cotter (3), J. Lincoln Foreman (2)
ABSTRACT
Paleosols with vertic (Vertisol-like) features occur in repetitively stacked fining-upward sequences bounded by marine erosional surfaces in the Bloomsburg Formation (Ludlovian to Pridolian) of central Pennsylvania. Paleosol development was strongly influenced by repeated changes in relative sea level, which resulted in subaerial exposure and pedogenesis of marginal-marine sediment accumulating along a low-energy, mud-dominated coastline in a delta-plain environment. Bloomsburg paleosols are characterized by very weak horizonation, abundant pedogenic slickensides, and a micromorphology dominated by sepic fabrics and peds bounded by stress cutans. Pedogenic carbonate is sparse, occurring principally as micrite nodules. Stable carbon isotope compositions of stratigraphically-low pedogen
c carbonate (mean 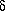 13C = -1.92
13C = -1.92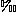 PDB) are attributed to pedogenesis proximal to a marine coastline. In stratigraphically-high paleosols showing evidence of rhizolith development, isotopic compositions of pedogenic carbonate suggest a significant contribution of carbon from C3 flora. Atmospheric P(CO2) levels estimated for these calcretes (4500-5500 ppmV) are significantly greater than present-day values. Low
PDB) are attributed to pedogenesis proximal to a marine coastline. In stratigraphically-high paleosols showing evidence of rhizolith development, isotopic compositions of pedogenic carbonate suggest a significant contribution of carbon from C3 flora. Atmospheric P(CO2) levels estimated for these calcretes (4500-5500 ppmV) are significantly greater than present-day values. Low 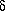 18O values for pedogenic carbonate (mean
18O values for pedogenic carbonate (mean 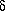 18O = -12.12
18O = -12.12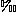 PDB) record
isotopic exchange between paleosol carbonate and 18O-enriched fluids associated with the conversion of original soil smectites to illite and chlorite during burial diagenesis. Paleosols bounded by marine erosional surfaces show variable degrees of marine hydromorphism attributable to rising water table during transgression', evidence for hydromorphism includes extensive reduction of iron as well as relative increases in CaO, MnO, MgO, P2O5, Na2O, and Sr at the tops of paleosols, due to introduction of marine fluids and sediment into open soil fractures and burrows. The abundance of vertic features in all Bloomsburg paleosols, by analogy with Holocene Vertisols, indicates the recurrence of a seasonally wet-dry (dry 4-8 months/year) paleoclimate
n the central Appalachian region at a paleolatitude of about 20° south.
PDB) record
isotopic exchange between paleosol carbonate and 18O-enriched fluids associated with the conversion of original soil smectites to illite and chlorite during burial diagenesis. Paleosols bounded by marine erosional surfaces show variable degrees of marine hydromorphism attributable to rising water table during transgression', evidence for hydromorphism includes extensive reduction of iron as well as relative increases in CaO, MnO, MgO, P2O5, Na2O, and Sr at the tops of paleosols, due to introduction of marine fluids and sediment into open soil fractures and burrows. The abundance of vertic features in all Bloomsburg paleosols, by analogy with Holocene Vertisols, indicates the recurrence of a seasonally wet-dry (dry 4-8 months/year) paleoclimate
n the central Appalachian region at a paleolatitude of about 20° south.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 | |
| Open PDF Document: $24 |
