About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Journal of Sedimentary Research (SEPM)
Abstract
Authigenic Carbonate Concretions and Host Shales from the Shimanto Belt, Southwestern Japan: Implications for Carbonate Precipitation
Kenichiro Sugitani (1) (*), Ryuichi Sugisaki (2), Mamoru  Adachi
Adachi (2)
(2)
ABSTRACT
Carbonate concretions and host shales from the Cretaceous Northern Shimanto Belt in southwestern Japan were studied. There are three types of carbonate concretions: spherical micritic, lenticular micritic, and lenticular crystalline. They contain calcite, clay minerals, framboidal pyrite, and detrital quartz and feldspar. The concretions have carbon isotopic compositions between -17.3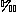 and -6.6
and -6.6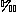 (PDB), reflecting the contribution of light carbon derived from organic matter. Distribution patterns of elements in the histogram of Al2O3/TiO2, and in the diagrams of Zr-TiO2, SiO2/TiO2-Al2O3/TiO2, and Zr-K2O-Rb suggest that the concretions contain more acidic tuff than do the host shales. Supply of acidic tuff to the site of deposition is also suggested by the presence of arcuate or cuspate detrital quartz grains in the samples. The formation of authigenic carbonates was probably related to an increase in influx of acidic tuff. In particular, the formation of the lenticular micritic concretions is a good representative.
(PDB), reflecting the contribution of light carbon derived from organic matter. Distribution patterns of elements in the histogram of Al2O3/TiO2, and in the diagrams of Zr-TiO2, SiO2/TiO2-Al2O3/TiO2, and Zr-K2O-Rb suggest that the concretions contain more acidic tuff than do the host shales. Supply of acidic tuff to the site of deposition is also suggested by the presence of arcuate or cuspate detrital quartz grains in the samples. The formation of authigenic carbonates was probably related to an increase in influx of acidic tuff. In particular, the formation of the lenticular micritic concretions is a good representative.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 | |
| Open PDF Document: $24 |

