About This Item
Share This Item
Abstract
Journal of Sedimentary Research, Section
A: Sedimentary Petrology and Processes
Vol. 66 (1996)No.
1. (January), Pages 139-146
Authigenic Feldspar as an Indicator of Paleo-Rock/Water Interactions in
Permian Carbonates of the Northern Calcareous Alps, Austria
Christoph Spotl (1), Martin Kralik (2), Michael J. Kunk
(3)
ABSTRACT
Dolostones interbedded with Upper Permian evaporites at the base of the
Northern Calcareous Alps contain abundant authigenic K-feldspar. Two petrographically,
structurally, and isotopically distinct generations of K-feldspar can be
distinguished: crystals composed of an inclusion. rich core and a clear
rim, and optically unzoned, transparent crystals. Both feldspar types have
essentially identical K-feldspar end-member compositions with >= 99.5 mole
% Or component. Low oxygen isotope ratios (+16.1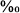 to +18.1
to +18.1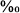 SMOW) suggest precipitation from 18O-enriched, saline fluids
at temperatures in excess of
SMOW) suggest precipitation from 18O-enriched, saline fluids
at temperatures in excess of 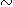 140°C. 40 r/39Ar plateau-age spectra of five
samples range from 145 ± 1 to 144 ±1 Ma (Early Berriasian)
and suggest that both types of feldspar were formed within an interval
that did not exceed
140°C. 40 r/39Ar plateau-age spectra of five
samples range from 145 ± 1 to 144 ±1 Ma (Early Berriasian)
and suggest that both types of feldspar were formed within an interval
that did not exceed 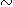 2 m.y. Rb/Sr model ages range from 152 to 140 Ma, assuming that the burial
diagenetic regime was buffered with respect to strontium by the associated
marine Permian evaporites. Authigenic K-feldspar records two distinct events
of hot brine flow, most likely triggered by tectonic movements (detachment)
and by an increase in the subsurface temperature in response to thrust
loading.
2 m.y. Rb/Sr model ages range from 152 to 140 Ma, assuming that the burial
diagenetic regime was buffered with respect to strontium by the associated
marine Permian evaporites. Authigenic K-feldspar records two distinct events
of hot brine flow, most likely triggered by tectonic movements (detachment)
and by an increase in the subsurface temperature in response to thrust
loading.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 |
Watermarked Document – A Watermarked Document is branded with the name of the original licensed customer to discourage unauthorized users from sharing the document outside the user's organization. The PDF is no longer restricted to one machine, but can be circulated to others in the same company or department. A Watermarked Document also can be printed for hard copy distribution internally but is not authorized for outside distribution nor posting on the internet. Users will not be able to cut-and-paste text or images from one document to another.
|
| Open PDF Document: $24 |
Open Document – An Open Document is a fully functional PDF that can be circulated (a digital copy or hard-copy printed documents) outside the purchasing organization. Purchase of an Open Document does NOT constitute license for republication in any form, nor does it allow web posting without prior written permission from AAPG/Datapages ([email protected]).
|
GIS Map Publishing Program
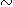 140°C. 40 r/39Ar plateau-age spectra of five
samples range from 145 ± 1 to 144 ±1 Ma (Early Berriasian)
and suggest that both types of feldspar were formed within an interval
that did not exceed
140°C. 40 r/39Ar plateau-age spectra of five
samples range from 145 ± 1 to 144 ±1 Ma (Early Berriasian)
and suggest that both types of feldspar were formed within an interval
that did not exceed 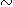 2 m.y. Rb/Sr model ages range from 152 to 140 Ma, assuming that the burial
diagenetic regime was buffered with respect to strontium by the associated
marine Permian evaporites. Authigenic K-feldspar records two distinct events
of hot brine flow, most likely triggered by tectonic movements (detachment)
and by an increase in the subsurface temperature in response to thrust
loading.
2 m.y. Rb/Sr model ages range from 152 to 140 Ma, assuming that the burial
diagenetic regime was buffered with respect to strontium by the associated
marine Permian evaporites. Authigenic K-feldspar records two distinct events
of hot brine flow, most likely triggered by tectonic movements (detachment)
and by an increase in the subsurface temperature in response to thrust
loading.
