The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
AAPG Bulletin
Figure
AAPG Bulletin; Year: 2015; Issue: June DOI: 10.1306/01191513191
Return to Full Text
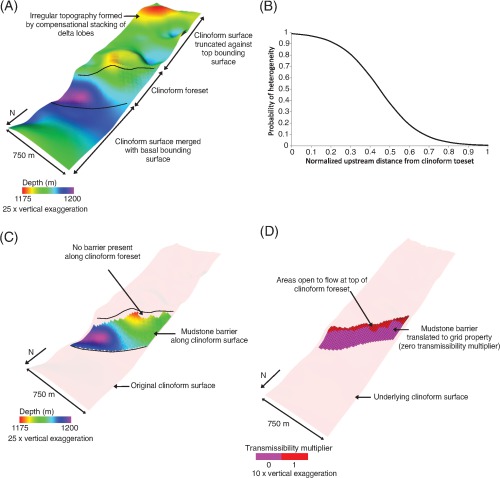
Figure 6
(A) Three-dimensional clinoform surface from parasequence 1.5 in the reservoir-scale model of the Ferron Sandstone Member (Figures 2B, 3B), generated using the clinoform-modeling algorithm of Graham et al. (2015, this volume). (B) The generic frequency function (equation 1) used to place elliptical barriers along each clinoform surface. Note the  axis is dimensionless and has been scaled between 0 and 1 so the same function can be applied to clinoforms with varying lengths. (C) Extent of overlapping elliptical barriers along the 3-D clinoform surface in part A. The barriers cover 80% of the clinoform surface. (D) The barrier-covered clinoform surface in part C is translated into a transmissibility multiplier grid property in
axis is dimensionless and has been scaled between 0 and 1 so the same function can be applied to clinoforms with varying lengths. (C) Extent of overlapping elliptical barriers along the 3-D clinoform surface in part A. The barriers cover 80% of the clinoform surface. (D) The barrier-covered clinoform surface in part C is translated into a transmissibility multiplier grid property in  ,
,  , and/or
, and/or 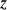 directions, depending on the orientation of the clinoform. The transmissibility multiplier is modified for cells in the grid layer above the clinoform surface. Grid cells in red are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 1 and are open to flow, whereas grid cells in purple are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 0 and act as a barrier to flow.
directions, depending on the orientation of the clinoform. The transmissibility multiplier is modified for cells in the grid layer above the clinoform surface. Grid cells in red are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 1 and are open to flow, whereas grid cells in purple are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 0 and act as a barrier to flow.

Figure 6
(A) Three-dimensional clinoform surface from parasequence 1.5 in the reservoir-scale model of the Ferron Sandstone Member (Figures 2B, 3B), generated using the clinoform-modeling algorithm of Graham et al. (2015, this volume). (B) The generic frequency function (equation 1) used to place elliptical barriers along each clinoform surface. Note the axis is dimensionless and has been scaled between 0 and 1 so the same function can be applied to clinoforms with varying lengths. (C) Extent of overlapping elliptical barriers along the 3-D clinoform surface in part A. The barriers cover 80% of the clinoform surface. (D) The barrier-covered clinoform surface in part C is translated into a transmissibility multiplier grid property in
,
, and/or
directions, depending on the orientation of the clinoform. The transmissibility multiplier is modified for cells in the grid layer above the clinoform surface. Grid cells in red are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 1 and are open to flow, whereas grid cells in purple are assigned a transmissibility multiplier of 0 and act as a barrier to flow.