About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Journal of Sedimentary Research (SEPM)
Abstract
Isotopic Composition of a Calcite-cemented Layer in the Lower Jurassic Bridport Sands, Southern England: Implications for Formation of Laterally Extensive Calcite-cemented Layers
Per Arne Bjorkum (1), Olav Walderhaug (2)
ABSTRACT
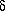 18OPDB and
18OPDB and 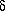 13CPDB values have been measured on 107 calcite cement samples from a laterally extensive (> 3 km) and continuous calcite-cemented layer 0.5 m thick in the coastal exposures of the Lower Jurassic shallow-marine Bridport Sands in Dorset, southern England. The samples were taken from a two-dimensional grid with 10-cm horizontal and vertical spacing between samples and along individual vertical lines across the calcite-cemented layer.
13CPDB values have been measured on 107 calcite cement samples from a laterally extensive (> 3 km) and continuous calcite-cemented layer 0.5 m thick in the coastal exposures of the Lower Jurassic shallow-marine Bridport Sands in Dorset, southern England. The samples were taken from a two-dimensional grid with 10-cm horizontal and vertical spacing between samples and along individual vertical lines across the calcite-cemented layer. 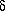 18OPDB values vary between -4.8
18OPDB values vary between -4.8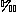 and -9.2
and -9.2 and decrease radially outwards from points with lateral spacings on the order of 0.5-1 m in the middle of the calcite-cemented layer. The
and decrease radially outwards from points with lateral spacings on the order of 0.5-1 m in the middle of the calcite-cemented layer. The 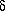 18OPDB values therefore indicate that the calcite-cemented layer was formed by merging of concretions. All
18OPDB values therefore indicate that the calcite-cemented layer was formed by merging of concretions. All 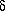 13CPDB values measured are in the narrow range -2.2
13CPDB values measured are in the narrow range -2.2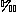 to -0.5
to -0.5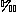 , which suggests that the dominant source of calcite cement in the layer was biogenic carbonate.
, which suggests that the dominant source of calcite cement in the layer was biogenic carbonate.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 | |
| Open PDF Document: $24 |
