About This Item
- Full TextFull Text(subscription required)
- Pay-Per-View PurchasePay-Per-View
Purchase Options Explain
Share This Item
The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
Journal of Sedimentary Research (SEPM)
Abstract
Petrographic and Geochemical Constraints on the Formation and Diagenesis of  Anhydrite
Anhydrite Cements, Smackover Sandstones, Gulf of Mexico
Cements, Smackover Sandstones, Gulf of Mexico
S. I. Dworkin (1), L. S. Land (2)
ABSTRACT
 Anhydrite
Anhydrite cement is common in sedimentary rocks, yet its origin is poorly understood. The high concentration of sulfate in sea water and the lack of appreciable sulfate in most other natural waters suggests that
cement is common in sedimentary rocks, yet its origin is poorly understood. The high concentration of sulfate in sea water and the lack of appreciable sulfate in most other natural waters suggests that  anhydrite
anhydrite cement may have a marine origin, but the relatively late timing of most anhydride cement tends to preclude sea water as the source of sulfate.
cement may have a marine origin, but the relatively late timing of most anhydride cement tends to preclude sea water as the source of sulfate.
 Anhydrite
Anhydrite cement is present in Upper Jurassic sandstones in the Gulf of Mexico as poikilotopic masses in which detrital grains are replaced and as smaller patches that have replaced single detrital grains.
cement is present in Upper Jurassic sandstones in the Gulf of Mexico as poikilotopic masses in which detrital grains are replaced and as smaller patches that have replaced single detrital grains.  Anhydrite
Anhydrite is a relatively late cement and postdates all other volumetrically significant authigenic phases, including K-feldspar, dolomite, quartz, and most calcite cements.
is a relatively late cement and postdates all other volumetrically significant authigenic phases, including K-feldspar, dolomite, quartz, and most calcite cements.
The expected isotopic composition and trace-element concentration of marine-derived Late Jurassic  anhydrite
anhydrite cement is predicted based on analyses of bedded
cement is predicted based on analyses of bedded  anhydrite
anhydrite and on analyses found in the literature. The expected chemical signature is:
and on analyses found in the literature. The expected chemical signature is: 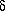 34S (
34S (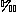 CDT) = +16,
CDT) = +16, 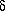 18O (
18O (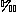 SMOW) = +14, 87Sr/86Sr = 0.7069, Sr = 1500-2500 ppm, Ba < 20 ppm, and Mg > 200 ppm. When geochemical analyses of Smackover
SMOW) = +14, 87Sr/86Sr = 0.7069, Sr = 1500-2500 ppm, Ba < 20 ppm, and Mg > 200 ppm. When geochemical analyses of Smackover  anhydrite
anhydrite cements are compared to the predicted composition, it is apparent that most of the cement is not of marine origin.
cements are compared to the predicted composition, it is apparent that most of the cement is not of marine origin.
Two generations of  anhydrite
anhydrite cement have been identified in the East Texas basin on the basis of their strontium isotopic compositions and their strontium concentrations. An early cement may have been derived from slightly modified Late Jurassic sea water, whereas a second group of cements may have precipitated later in the burial history or may represent recrystallization of the first cement. The chemistry of Louisiana and Mississippi basin
cement have been identified in the East Texas basin on the basis of their strontium isotopic compositions and their strontium concentrations. An early cement may have been derived from slightly modified Late Jurassic sea water, whereas a second group of cements may have precipitated later in the burial history or may represent recrystallization of the first cement. The chemistry of Louisiana and Mississippi basin  anhydrite
anhydrite cements indicates that the sulfate was derived from dissolved bedded
cements indicates that the sulfate was derived from dissolved bedded  anhydrite
anhydrite and was reprecipitated in the sandstones from fluids that had undergone extensive water-rock interaction after considerable burial. This study suggests that late
and was reprecipitated in the sandstones from fluids that had undergone extensive water-rock interaction after considerable burial. This study suggests that late  anhydrite
anhydrite cements in sedimentary rocks are most likely derived from remobilized calcium sulfate de
osits.
cements in sedimentary rocks are most likely derived from remobilized calcium sulfate de
osits.
Pay-Per-View Purchase Options
The article is available through a document delivery service. Explain these Purchase Options.
| Watermarked PDF Document: $14 | |
| Open PDF Document: $24 |
