The AAPG/Datapages Combined Publications Database
AAPG Bulletin
Figure
AAPG Bulletin; Year: 2019; Issue: April DOI: 10.1306/09181818025
Return to Full Text
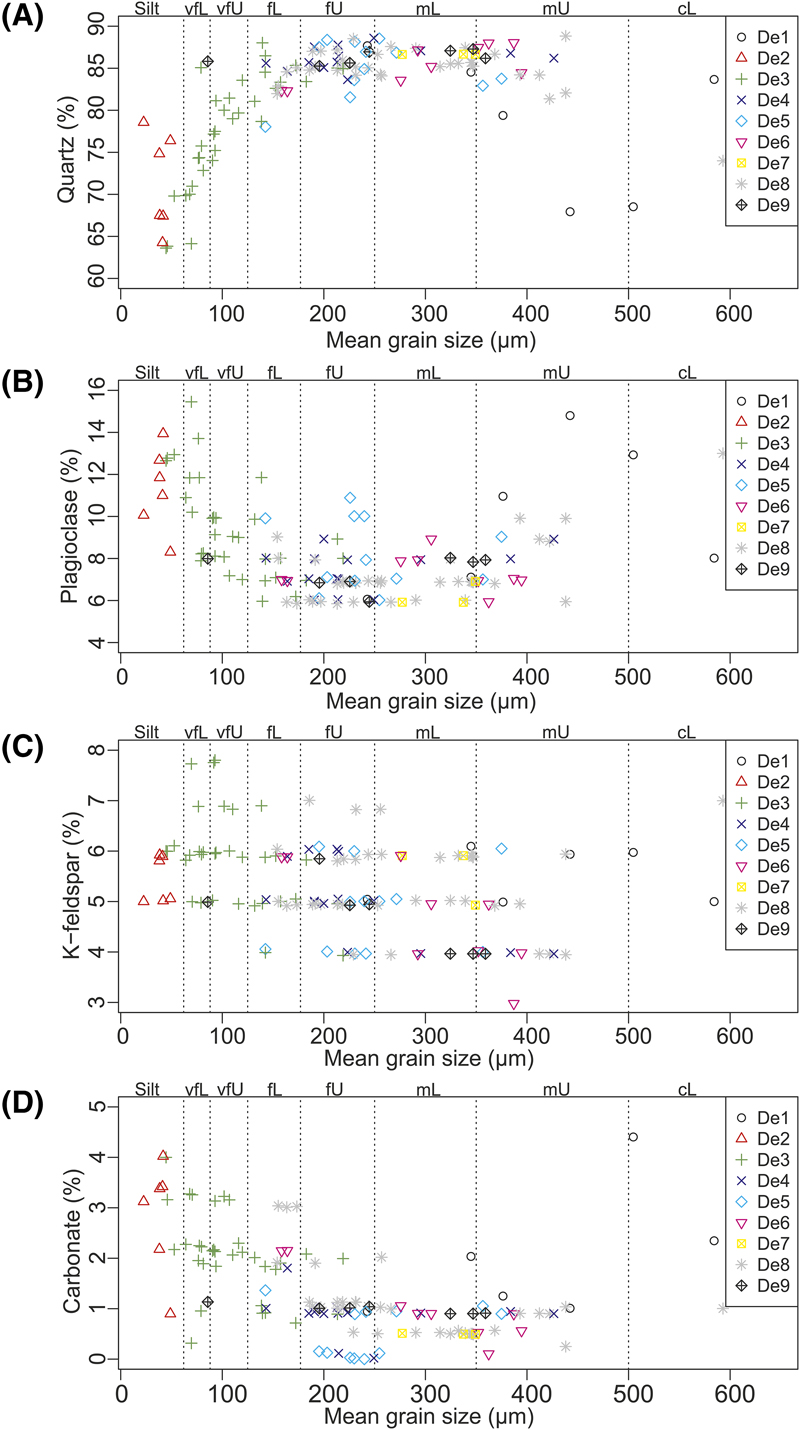
Figure 11. The relationship between specific mineral abundance and mean grain size, colored as a function of depositional environment. (A) Quartz, (B) plagioclase, (C) K-feldspar, and (D) carbonate. Note that quartz abundance increases with an increase in mean grain size, whereas plagioclase and carbonate abundance typically decrease. The K-feldspar abundance slightly decreases with an increase in mean grain size. Depositional environments are labeled accordingly: gravel bed (De1); mud flat (De2); mixed flat (De3); sand flat (De4); tidal bars and dunes (De5); tidal inlet (De6); backshore (De7); foreshore (De8); and proebb delta (De9). Mean grain-size classes are labeled accordingly: silt; lower very fine sand (vfL); upper very fine sand (vfU); lower fine sand (fL); upper fine sand (fU); lower medium sand (mL); upper medium sand (mU); and lower coarse sand (cL).

Figure 11. The relationship between specific mineral abundance and mean grain size, colored as a function of depositional environment. (A) Quartz, (B) plagioclase, (C) K-feldspar, and (D) carbonate. Note that quartz abundance increases with an increase in mean grain size, whereas plagioclase and carbonate abundance typically decrease. The K-feldspar abundance slightly decreases with an increase in mean grain size. Depositional environments are labeled accordingly: gravel bed (De1); mud flat (De2); mixed flat (De3); sand flat (De4); tidal bars and dunes (De5); tidal inlet (De6); backshore (De7); foreshore (De8); and proebb delta (De9). Mean grain-size classes are labeled accordingly: silt; lower very fine sand (vfL); upper very fine sand (vfU); lower fine sand (fL); upper fine sand (fU); lower medium sand (mL); upper medium sand (mU); and lower coarse sand (cL).